“STEAM€ and “STEM€…These words plaster the walls of educational institutions, libraries, and museums everywhere. One of the biggest curriculum introductions and implementations to date has been STEAM education. In fact, your child is most likely being taught this curriculum at their school on a daily basis. With that being said, many parents are still struggling to grasp what STEAM curriculum is.
So what really is STEAM education?

What is STEAM Education?
These terms describe curriculum that is based on the idea of educating students in either four or five categories (depending on which acronym is being referenced), science, technology, engineering, art, and mathematics. This clever curriculum-based acronym was first introduced by the National Science Foundation. The need for STEAM education was a result of educators wanting to prepare the next generation of the global workforce to create relevant jobs and drive the economy.
We know what you are thinking, “Haven’t these concepts and subjects been taught for decades?€
The answer is yes, but not in the way that the STEAM curriculum approaches it. Instead of teaching all concepts separately, STEAM education integrates them all into one cohesive learning experience that is based on real-world applications. Brilliant, right!?
€
What is the STEAM Process?
Now that we know what STEAM education is, we can focus on the process that drives STEAM education. STEAM’s foundations are based on inquiry, critical thinking, curiosity, and processed-based learning. It’s important to note that the entire idea surrounding STEAM education, lessons, and the overall approach is that it is fundamentally based around questioning.
The purpose of STEAM/STEM is to be able to find the answers and solutions to problems/questions using and integrating the fundamentals of the STEAM process.
Like any process, the STEAM education process follows a series of actions and steps. The steps that are followed vary depending on the educator, but all have the common end goal of solving a problem.
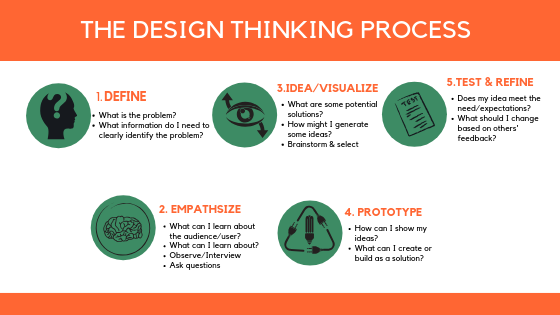
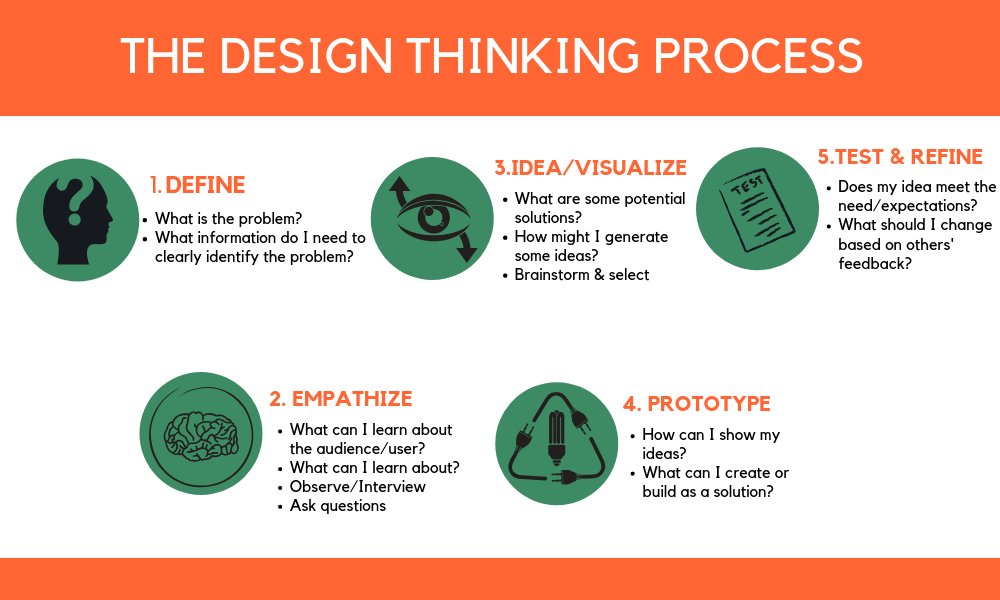
Often, when STEAM education is being taught, educators reference the “Design Thinking Process€. The Design Thinking Process consists of the following steps: define & observe, empathize, visualize, create a prototype, and test & refine.

€
Why Add the “A€ in STEAM Education?
Prior to adopting the acronym “STEAM€, the word “STEM€ was used to describe the curriculum. The “A€ in STEAM, as mentioned earlier, stands for the arts.
You might be thinking, “What does art have to do with STEAM education?€ and we’ve got an answer for you– The arts are a vital component of the STEAM process because STEAM-related products and designs are built according to creative and artistic designs.
This is where the interdisciplinary ability of STEAM concepts becomes extremely important in education.
In an article published by EdWeek.org they explain that “Art can serve a practical function. Students might apply design and decoration to products that were created during the course of a design challenge. They could use computer graphics to create logos or stylized designs to include in communications or presentations. Through industrial design, students could improve the appearance, design, and usability of a product created during a STEM project.€
As a result of this, it is much easier for scientific developments using the STEAM process to be communicated by integrating the arts, thus further stressing the importance of the “A€ in STEAM education.

€
STEAM Education in The Future
The growing movement of teaching STEAM education to primary and higher education is quickly gaining traction (and for a good reason). Students being taught on the concepts associated with STEAM education are not just learning the subject matter, but are being taught how to implement the interdisciplinary subjects in their everyday lives and careers.